The surface of Mars is littered with examples of glacier-like landforms. While surface ice deposits are mostly limited to the polar caps, patterns of slow, viscous flow abound in many non-polar regions of Mars. Streamlines that appear as linear ridges in the surface soils and rocky debris are often exposed on top of infilling deposits that coat crater and valley floors. We see such patterns on the surfaces of Earth’s icy glaciers and debris-covered “rock glaciers.” As ice flows downhill, rock and soil are plucked from the surrounding landscape and ferried along the flowing ice surface and within the icy subsurface. While this process is gradual, taking perhaps thousands of years or longer, it creates a network of linear patterns that reveal the history of ice flow.
Related posts
-

Marvel delays ‘Avengers: Doomsday’ and ‘Avengers: Secret Wars’ by 7 months each
Marvel maniacs are going to have to muster more patience to watch “Avengers: Doomsday” and “Avengers:... -
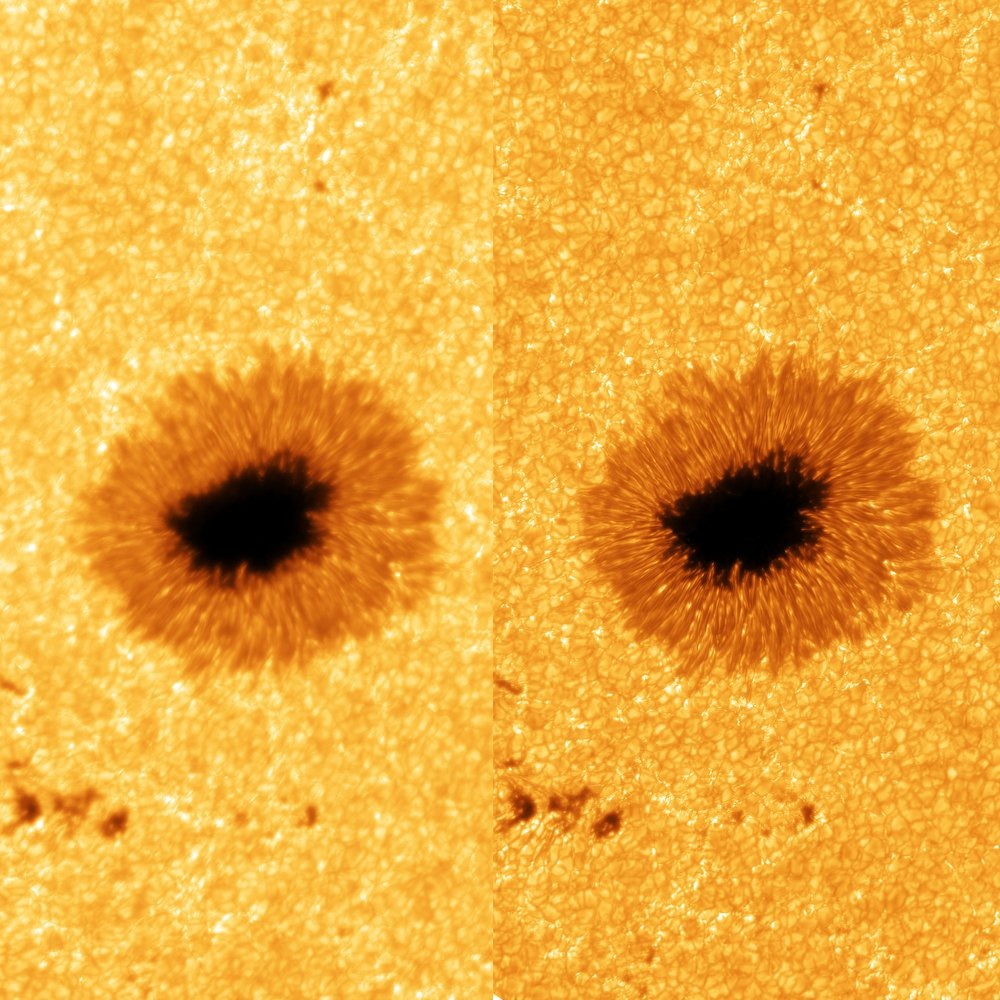
New 8K-resolution photos of the sun show off incredible details of raging sunspots
Incredible new images of the sun’s surface provide an unprecedented view of raging sunspots and solar... -
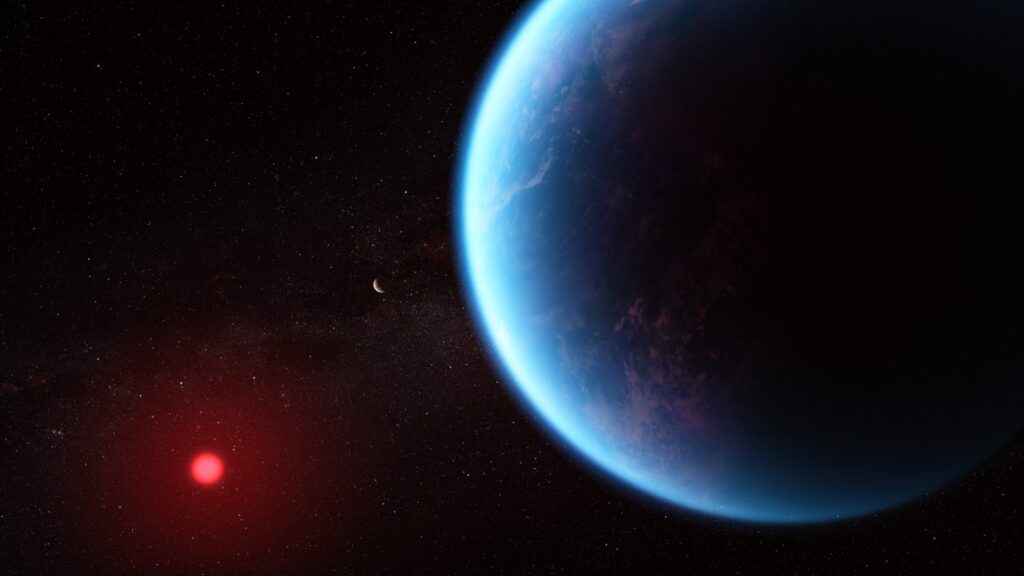

Scientists question possible signs of life on exoplanet K2-18b in new study: ‘We never saw more than insignificant hints’
In 2023, scientists from Cambridge University reported what appeared to be very exciting news. NASA’s James...